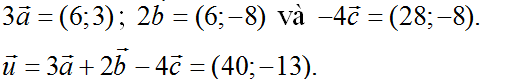Cho \(\overrightarrow{a}=\left(1;5\right)\), \(\overrightarrow{b}=\left(-2;1\right)\). Tính \(\overrightarrow{c}=3\overrightarrow{a}+2\overrightarrow{b}\)

Những câu hỏi liên quan
Cho overrightarrow{a}left(2;1right);overrightarrow{b}left(3;-4right);overrightarrow{c}left(-7;2right)
a) Tìm tọa độ của vectơ overrightarrow{u}3overrightarrow{a}+2overrightarrow{b}-4overrightarrow{c}
b) Tìm tọa độ vectơ overrightarrow{x} sao cho : overrightarrow{x}+overrightarrow{a}overrightarrow{b}-overrightarrow{c}
c) Tìm các số k và h sao cho : overrightarrow{c}koverrightarrow{a}+hoverrightarrow{b}
Đọc tiếp
Cho \(\overrightarrow{a}=\left(2;1\right);\overrightarrow{b}=\left(3;-4\right);\overrightarrow{c=}\left(-7;2\right)\)
a) Tìm tọa độ của vectơ \(\overrightarrow{u}=3\overrightarrow{a}+2\overrightarrow{b}-4\overrightarrow{c}\)
b) Tìm tọa độ vectơ \(\overrightarrow{x}\) sao cho : \(\overrightarrow{x}+\overrightarrow{a}=\overrightarrow{b}-\overrightarrow{c}\)
c) Tìm các số k và h sao cho : \(\overrightarrow{c}=k\overrightarrow{a}+h\overrightarrow{b}\)
a) \(\overrightarrow{u}=3\overrightarrow{a}+2\overrightarrow{b}-4\overrightarrow{c}=3\left(2;1\right)+2\left(3;-4\right)-4\left(-7;2\right)\)
\(=\left(6;3\right)+\left(6;-8\right)-\left(-28;8\right)\)
\(=\left(6+6+28;3-8-8\right)=\left(40;-13\right)\).
b) \(\overrightarrow{x}+\overrightarrow{a}=\overrightarrow{b}-\overrightarrow{c}\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{x}=\overrightarrow{b}-\overrightarrow{c}-\overrightarrow{a}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{x}=\left(3;-4\right)-\left(-7;2\right)-\left(2;1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{x}=\left(3+7-2;-4-2-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{x}=\left(8;-7\right)\).
c) Có \(\overrightarrow{c}\left(-7;2\right)=k\overrightarrow{a}+h\overrightarrow{b}=k\left(2;1\right)+h\left(3;-4\right)\)
\(=\left(2k+3h;k-4h\right)\).
Từ đó suy ra: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2k+3h=-7\\k-4h=2\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}k=-2\\h=-1\end{matrix}\right.\).
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho overrightarrow{a}left(2;1right);overrightarrow{b}left(3;-4right);overrightarrow{c}left(-7;2right)
a) Tìm tọa độ của vectơ overrightarrow{u}3overrightarrow{a}+2overrightarrow{b}-4overrightarrow{c}
b) Tìm tọa độ của vectơ overrightarrow{x} sao cho overrightarrow{x}+overrightarrow{a}overrightarrow{b}-overrightarrow{c}
c) Tìm các số k và h sao cho overrightarrow{c}koverrightarrow{a}+hoverrightarrow{b}
Đọc tiếp
Cho \(\overrightarrow{a}=\left(2;1\right);\overrightarrow{b}=\left(3;-4\right);\overrightarrow{c}=\left(-7;2\right)\)
a) Tìm tọa độ của vectơ \(\overrightarrow{u}=3\overrightarrow{a}+2\overrightarrow{b}-4\overrightarrow{c}\)
b) Tìm tọa độ của vectơ \(\overrightarrow{x}\) sao cho \(\overrightarrow{x}+\overrightarrow{a}=\overrightarrow{b}-\overrightarrow{c}\)
c) Tìm các số k và h sao cho \(\overrightarrow{c}=k\overrightarrow{a}+h\overrightarrow{b}\)
Cho hai vecto \(\overrightarrow{a}\) và \(\overrightarrow{b}\). Biết \(\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|=2,\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|=\sqrt{3}\) và \(\left(\overrightarrow{a},\overrightarrow{b}\right)\)=30 độ. Tính \(\left|\overrightarrow{a} \over...
Xem chi tiết
Tính \(\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}\) hả bạn?
\(\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|.\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|cos\left(\overrightarrow{a};\overrightarrow{b}\right)=2.\sqrt{3}.cos30^0=3\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (1)
Đặt \(A=\left|\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right|\Rightarrow A^2=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|^2+\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2+2\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|.\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|.cos\left(\overrightarrow{a};\overrightarrow{b}\right)\)
\(=2^2+3+2.2.\sqrt{3}.cos30^0=13\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right|=\sqrt{13}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho ba vecto \(\overrightarrow{a}=\left(-2;1\right),\overrightarrow{b}=\left(1;3\right),\overrightarrow{c}=\left(-3;3\right)\). Hãy phân tích vecto \(\overrightarrow{c}\)thep 2 vecto \(\overrightarrow{a};\overrightarrow{b}\)
Cho 3 vectơ \(\overrightarrow{a},\overrightarrow{b},\overrightarrow{c}\) tuỳ ý. Chứng minh:
\(\left|\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}\right|\le\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|+\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|+\left|\overrightarrow{c}\right|\). Dấu "=" xảy ra khi nào? Nêu bài toán tổng quát
Lời giải:
Xét hai vecto bất kỳ \(\overrightarrow{AB}, \overrightarrow{CD}\). Kẻ vecto $\overrightarrow{CT}$ sao cho $\overrightarrow{CT}=\overrightarrow{BA}$
Ta có:
\(|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{CD}|=|\overrightarrow{TC}+\overrightarrow{CD}|=|\overrightarrow{TD}|\)
\(|\overrightarrow{AB}|+|\overrightarrow{CD}|=|\overrightarrow{TC}|+|\overrightarrow{CD}|\)
Mà theo bđt tam giác thì:
\(|\overrightarrow{TC}+\overrightarrow{CD}|\geq |\overrightarrow{TD}|\Rightarrow |\overrightarrow{AB}|+\overrightarrow{CD}|\geq |\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{CD}|\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(T, C,D\) thẳng hàng và $C$ nằm giữa $T,D$
$\Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow{TC}, \overrightarrow{CD}$ cùng hướng
$\Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow{AB}, \overrightarrow{CD}$ cùng hướng
Vậy với $\overrightarrow{a}, \overrightarrow{b}$ bất kỳ thì $|\overrightarrow{a}|+|\overrightarrow{b}|\geq |\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}|$. Dấu "=" xảy ra khi $\overrightarrow{a}, \overrightarrow{b}$ cùng hướng.
------------------
Áp dụng vào bài toán:
\(|\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}|\leq |\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}|+|\overrightarrow{c}|\leq |\overrightarrow{a}|+|\overrightarrow{b}|+|\overrightarrow{c}|\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(\overrightarrow{a}, \overrightarrow{b}\) cùng hướng và \(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}, \overrightarrow{c}\) cùng hướng
\(\Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow{a}, \overrightarrow{b}, \overrightarrow{c}\) cùng hướng
Đúng 1
Bình luận (0)
Cho các vecto \(\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|=x,\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|=y,\left|\overrightarrow{z}\right|=c\) và vecto a+b+3c=0. Tính \(A=\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{b}.\overrightarrow{c}+\overrightarrow{c}.\overrightarrow{a}\)
\(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+3\overrightarrow{c}=\overrightarrow{0}\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}=-2\overrightarrow{c}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{c}\right)^2=\left(-2\overrightarrow{c}\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{a}^2+\overrightarrow{b}^2+\overrightarrow{c}^2+2\left(\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{b}.\overrightarrow{c}+\overrightarrow{c}.\overrightarrow{a}\right)=4\overrightarrow{c}^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{4x^2-\left(x^2+y^2+z^2\right)}{2}=\dfrac{3x^2-y^2-z^2}{2}\)
Đúng 2
Bình luận (0)
Áp dụng tính chất giao hoán và tính chất phân phối của tích vô hướng hãy chứng minh các kết quả sau đây :
left(overrightarrow{a}+overrightarrow{b}right)^2left|overrightarrow{a}right|^2+left|overrightarrow{b}right|^2+2overrightarrow{a}.overrightarrow{b}
left(overrightarrow{a}-overrightarrow{b}right)^2left|overrightarrow{a}right|^2+left|overrightarrow{b}right|^2-2overrightarrow{a}.overrightarrow{b}
left(overrightarrow{a}+overrightarrow{b}right)left(overrightarrow{a}-overrightarrow{b}right)left|...
Đọc tiếp
Áp dụng tính chất giao hoán và tính chất phân phối của tích vô hướng hãy chứng minh các kết quả sau đây :
\(\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)^2=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|^2+\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2+2\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}\)
\(\left(\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}\right)^2=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|^2+\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2-2\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}\)
\(\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}\right)=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|^2-\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2\)
\(\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)^2=\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)\)\(=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|^2+\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2+2\overrightarrow{a}\overrightarrow{b}\).
\(\left(\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}\right)^2=\left(\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}\right)\)\(=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|^2+\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2-2\overrightarrow{a}\overrightarrow{b}\).
\(\left(\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b}\right)\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|^2+\overrightarrow{a}\overrightarrow{b}-\overrightarrow{a}\overrightarrow{b}+\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2\)\(=\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|^2-\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|^2\).
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Cho các véctơ overrightarrow{a},overrightarrow{b},overrightarrow{c} thỏa mãn left|overrightarrow{a}right|x,left|overrightarrow{b}right|y,left|overrightarrow{c}right|z và overrightarrow{a}+overrightarrow{b}+3overrightarrow{c}overrightarrow{0} Tính Aoverrightarrow{a}.overrightarrow{b}+overrightarrow{b}.overrightarrow{c}+overrightarrow{c}.overrightarrow{a}
Đọc tiếp
Cho các véctơ \(\overrightarrow{a},\overrightarrow{b},\overrightarrow{c}\) thỏa mãn \(\left|\overrightarrow{a}\right|=x,\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|=y,\left|\overrightarrow{c}\right|=z\) và \(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+3\overrightarrow{c}=\overrightarrow{0}\) Tính \(A=\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}+\overrightarrow{b}.\overrightarrow{c}+\overrightarrow{c}.\overrightarrow{a}\)
Ta có:
\(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}+3\overrightarrow{c}=\overrightarrow{0}\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}=-3\overrightarrow{c}\Leftrightarrow\left(\overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b}\right)^2=9\overrightarrow{c}^2\)
<=> \(\overrightarrow{a}^2+\overrightarrow{b}^2+2\overrightarrow{a}\overrightarrow{b}=9\overrightarrow{c}^2\)
<=> \(\overrightarrow{a}\overrightarrow{b}=\dfrac{9z^2-x^2-y^2}{2}\)
Tương tự ta có: \(\overrightarrow{b}+3\overrightarrow{c}=-\overrightarrow{a}\) <=> \(\left(\overrightarrow{b}+3\overrightarrow{c}\right)^2=\overrightarrow{a}^2\)
<=> \(\overrightarrow{b}.\overrightarrow{c}=\dfrac{x^2-y^2-9z^2}{2}\)
Và lại có : \(\overrightarrow{a}\overrightarrow{c}=\dfrac{y^2-x^2-9z^2}{2}\)
Suy ra: A=\(\dfrac{9z^2-x^2-y^2}{2}+\dfrac{x^2-y^2-9z^2}{2}+\dfrac{y^2-x^2-9z^2}{2}=\dfrac{3z^2-z^2-y^2}{2}\)
Đúng 0
Bình luận (0)
Bài 3. (1 điểm) Cho hai vectơ $\overrightarrow{a}$ và $\overrightarrow{b}$ thỏa mãn: $\left| \overrightarrow{a} \right|=1, \, \left| \overrightarrow{b} \right|=2, \, \left| \overrightarrow{a}-2\overrightarrow{b} \right|=\sqrt{15}.$
a) Tính $\overrightarrow{a}.\overrightarrow{b}$.
b) Xác định $k$ để góc giữa $\left( \overrightarrow{a}+\overrightarrow{b} \right)\left( 2k\overrightarrow{a}-\overrightarrow{b} \right)$ bằng ${{60}^{\circ }}$.